 | Javascript object and Properties | Best Practices for DOM Operations |  |
Javascript: DOM Manipulation Basics |
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming interface for web documents. It represents the page as a tree of objects, where each HTML element is a node. JavaScript can use the DOM to access and change content, structure, and styles.
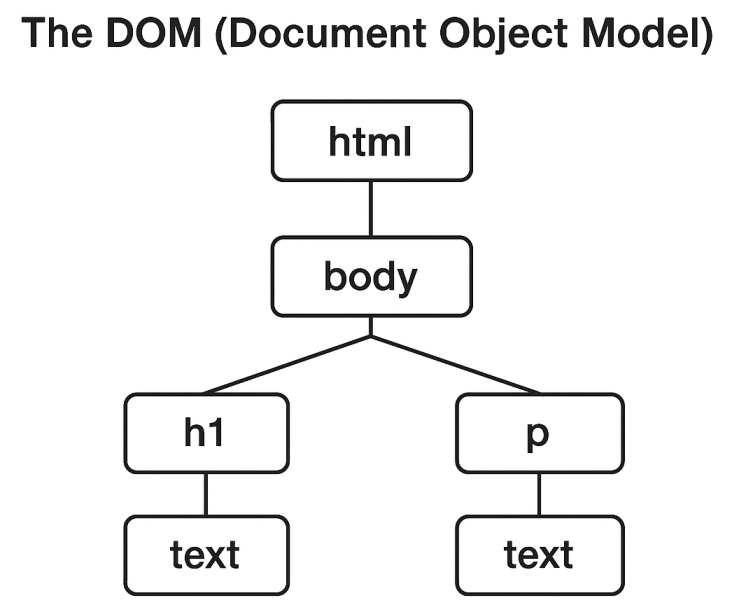
The Document Object Model (DOM) represents an HTML document as a tree of nodes. Below is a simple visual diagram showing how elements are organized in the DOM tree.
// Get an element by id
const el = document.getElementById('my-element');
// Query selector
const firstParagraph = document.querySelector('main article p');
// Create and append an element
const p = document.createElement('p');
p.textContent = 'New paragraph';
document.querySelector('main article').appendChild(p);
// Modify attributes
el.setAttribute('data-role', 'demo');
// Remove an element
const node = document.querySelector('aside');
if(node) node.parentNode.removeChild(node);
Use developer tools (Inspect) in your browser to view the live DOM tree and experiment with these commands in the Console.
// By ID
const header = document.getElementById("mainTitle");
// By class
const items = document.getElementsByClassName("list-item");
// By tag
const paragraphs = document.getElementsByTagName("p");
// Modern query selectors
const firstItem = document.querySelector(".list-item");
const allItems = document.querySelectorAll(".list-item");
document.getElementById("mainTitle").innerHTML = "New Title";
document.getElementById("mainTitle").textContent = "Plain Text Title";
const link = document.getElementById("myLink");
link.href = "https://example.com";
link.target = "_blank";
const box = document.getElementById("box");
box.style.backgroundColor = "lightblue";
box.style.fontSize = "20px";
// Create new element
const newItem = document.createElement("li");
newItem.textContent = "New List Item";
// Append to list
document.getElementById("myList").appendChild(newItem);
// Remove element
const oldItem = document.getElementById("removeMe");
oldItem.remove();
const button = document.getElementById("myButton");
button.addEventListener("click", function() {
alert("Button clicked!");
});
getElementById("id") → Selects a single element by its ID.querySelector("selector") → Selects the first element matching a CSS selector (.class, #id, tag).textContent sets plain text, innerHTML can insert HTML tags..style.property → Directly changes inline styles of an element.You can combine these with event listeners to make pages interactive.
Click the button to add a new item to the list.
 | Javascript object and Properties | Best Practices for DOM Operations |  |